Last Update: 8/15
双链表的应用在内核中随处可见,list.h头文件集中定义了双链表(struct list_head结构体)的相关操作。比如这里的一个头文件中就有大量的struct list_head型的数据。
关于list.h的分析,网上资料很多,这里只是记录我在分析list.h中遇到的问题。
0.struct list_head结构体
可能这样写,更让我们习惯:
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next;
struct list_head *prev;
};
这个结构经常作为成员与其他数据类型一起组成一个新的结构体(后文若无特别提示,“新结构体”均指类似下面举例的嵌套型结构体),比如:
struct stu
{
char name[20];
int id;
struct list_head list;
}
我们已经看到,struct list_head这个结构比较特殊,它内部没有任何数据,只是起到链接链表的作用。对于它当前所在的这个结点来说,next指向下一个结点,prev指向上一个结点。通常我们通过指向struc list_head的指针pos来获取它所在结点的地址,尽而获取其他数据。也许你现在还比较困惑这一过程,别着急,后面有特别解释。
1.链表的初始化
其实可以从后往前看,这样更容易理解。INIT_LIST_HEAD函数形成一个空链表。这个list变量一般作为头指针(非头结点)。
28static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
29{
30 list->next = list;
31 list->prev = list;
32}
下面的宏生成一个头指针name,如何生成?请看LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)。
25#define LIST_HEAD(name) \ 26 struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)将name的地址直接分别赋值给next和prev,那么它们事实上都指向自己,也形成一个空链表。现在再回头看宏LIST_HEAD(name),它其实就是一个定义并初始化作用。
23#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
3.添加元素
这两个函数分别给链表头结点后,头结点前添加元素。前者可实现栈的添加元素,后者可实现队列的添加元素。
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head);
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head);
这两个函数如何实现的?它们均调用的下面函数:
41static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
42 struct list_head *prev,
43 struct list_head *next)
44{
45 next->prev = new;
46 new->next = next;
47 new->prev = prev;
48 prev->next = new;
49}
现在我们要关注的是,list_add和list_add_tail两函数在调用__list_add函数时,对应的各个参数分别是什么?通过下面所列代码,我们可以发现这里的参数运用的很巧妙,类似JAVA中的封装。
64static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
65{
66 __list_add(new, head, head->next);
67}
78static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
79{
80 __list_add(new, head->prev, head);
81}
注意,这里的形参prev和next是两个连续的结点。这其实是数据结构中很普通的双链表元素添加问题,在此不再赘述。下面的图可供参考,图中1~4分别对应__list_add函数的四条语句。
这里又是一个调用关系,__list_del函数具体的过程很简单,分别让entry节点的前后两个结点(prev和next)“越级”指向彼此。请注意这个函数的后两句话,它属于不安全的删除。
103static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
104{
105 __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
106 entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
107 entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
108}
想要安全的删除,那么可以调用下面函数。还记得INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry)吗,它可以使entry节点的两个指针指向自己。
140static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
141{
142 __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
143 INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
144}
4.替换元素
用new结点替换old结点同样很简单,几乎是在old->prev和old->next两结点之间插入一个new结点。画图即可理解。
120static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
121 struct list_head *new)
122{
123 new->next = old->next;
124 new->next->prev = new;
125 new->prev = old->prev;
126 new->prev->next = new;
127}
同样,想要安全替换,可以调用:
129static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
130 struct list_head *new)
131{
132 list_replace(old, new);
133 INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
134}
5.移动元素
理解了删除和增加结点,那么将一个节点移动到链表中另一个位置,其实就很清晰了。list_move函数最终调用的是__list_add(list,head,head->next),实现将list移动到头结点之后;而list_move_tail函数最终调用__list_add_tail(list,head->prev,head),实现将list节点移动到链表末尾。
151static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
152{
153 __list_del(list->prev, list->next);
154 list_add(list, head);
155}
156
162static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
163 struct list_head *head)
164{
165 __list_del(list->prev, list->next);
166 list_add_tail(list, head);
167}
6.测试函数
接下来的几个测试函数,基本上是“代码如其名”。
list_is_last函数是测试list是否为链表head的最后一个节点。
174static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,
175 const struct list_head *head)
176{
177 return list->next == head;
178}
下面的函数是测试head链表是否为空链表。注意这个list_empty_careful函数,他比list_empty函数“仔细”在那里呢?前者只是认为只要一个结点的next指针指向头指针就算为空,但是后者还要去检查头节点的prev指针是否也指向头结点。另外,这种仔细也是有条件的,只有在删除节点时用list_del_init(),才能确保检测成功。
184static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
185{
186 return head->next == head;
187}
202static inline int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head)
203{
204 struct list_head *next = head->next;
205 return (next == head) && (next == head->prev);
206}
下面的函数是测试head链表是否只有一个结点:这个链表既不能是空而且head前后的两个结点都得是同一个结点。
226static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head)
227{
228 return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
229}
7.将链表左转180度
正如注释说明的那样,此函数会将这个链表以head为转动点,左转180度。整个过程就是将head后的结点不断的移动到head结点的最左端。如果是单个结点那么返回真,否则假。
212static inline void list_rotate_left(struct list_head *head)
213{
214 struct list_head *first;
215
216 if (!list_empty(head)) {
217 first = head->next;
218 list_move_tail(first, head);
219 }
220}
上述函数每次都调用 list_move_tail(first, head);其实我们将其分解到“最小”,那么这个函数每次最终调用的都是:__list_del(first->prev,first->next);和__list_add(list,head->prev,head);这样看起来其实就一目了然了。
8.将链表一分为二
这个函数是将head后至entry之间(包括entry)的所有结点都“切开”,让他们成为一个以list为头结点的新链表。我们先从宏观上看,如果head本身是一个空链表则失败;如果head是一个单结点链表而且entry所指的那个结点又不再这个链表中,也失败;当entry恰好就是头结点,那么直接初始化list,为什么?因为按照刚才所说的切割规则,从head后到entry前事实上就是空结点。如果上述条件都不符合,那么就可以放心的“切割”了。
257static inline void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
258 struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
259{
260 if (list_empty(head))
261 return;
262 if (list_is_singular(head) &&
263 (head->next != entry && head != entry))
264 return;
265 if (entry == head)
266 INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
267 else
268 __list_cut_position(list, head, entry);
269}
具体如何切割,这里的代码貌似很麻烦,可是我们画出图后,就“一切尽在不言中”了。
231static inline void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,
232 struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
233{
234 struct list_head *new_first = entry->next;
235 list->next = head->next;
236 list->next->prev = list;
237 list->prev = entry;
238 entry->next = list;
239 head->next = new_first;
240 new_first->prev = head;
241}
图示:
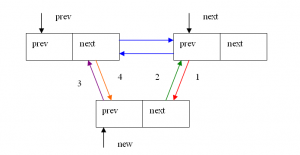
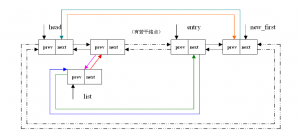
 看来以后要多锻炼锻炼!不能只会写不会说!我不要做刘永苹(这位老师理论知识充裕,但是表达严重不靠谱)!
看来以后要多锻炼锻炼!不能只会写不会说!我不要做刘永苹(这位老师理论知识充裕,但是表达严重不靠谱)!